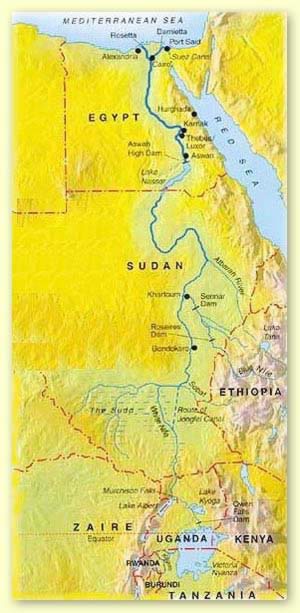
The
Nile is the
longest river in the world,
stretching north for approximately 4,000 miles from East Africa to the
Mediterranean. Studies have shown that the River (Iteru, meaning,
simply, River, as the Map of the Nile RiverEgyptians called it)
gradually changed its location and size over millions of years. The Nile
flows from the mountains in the south to the Mediterranean in the
north. Egyptians traveling to other lands would comment on the "wrong"
flow of other rivers. For example, a text of Tuthmosis I in Nubia
describes the great Euphrates river as the "inverted water that goes
downstream in going upstream."
Three rivers flowed into the Nile from the south and thus served as its
sources: the Blue Nile, the White Nile and the Arbara. Within the
southern section between Aswan and Khartoum, land which was called
Nubia, the River passes through formations of hard igneous rock,
resulting in a series of rapids, or cataracts, which form a natural
boundary to the south. Between the first and second cataracts lay Lower
Nubia, and between the second and sixth cataracts lay upper Nubia.
Along most of its length through Egypt, the Nile has scoured a deep,
wide gorge in the desert plateau. At Aswan North of the first cataract
the Nile is deeper and its surface smoother. Downstream from Aswan the
Nile flows northerly to Armant before taking a sharp bend, called the
Qena. From Armant to Hu, the River extends about 180 kilometers and
divides the narrow southern valley from the wider northern valley.
Southern Egypt, thus being upstream, is called Upper Egypt, and northern
Egypt, being downstream and the Delta, is called Lower Egypt. In
addition to the Valley and the Delta, the Nile also divided Egypt into
the Eastern and Western Deserts.
The Nile Just South of AswanThe Nile Valley is a canyon running 660
miles long with a floodplain occupying 4,250 square miles. The Delta
spans some 8,500 square miles and is fringed in its coastal regions by
lagoons, wetlands, lakes and sand dunes.
The Delta represented 63 percent of the inhabited area of Egypt,
extending about 200 kilometers from south to north and roughly 400
kilometers from east to west. While today the Nile flows through the
Delta in only two principal branches, the Damietta and the Rosetta, in
ancient times there were three principal channels, known as the water of
Pre, the water of Ptah and the water of Amun. In classical or
Graeco-Roman times, these were called the Pelusiac, the Sebennytic, and
the Canopic branches. There were additionally subsidiary branches or
artificially cut channels.
The most dominant features of the Delta as the sandy mounds of clay and
silt that appear as islands rising 1-12 meters above the surrounding
area. Since these mounds would not be submerged by the inundation, they
were ideal sites for Predynastic and Early Dynastic A modern sailboat on
the Nile, with a not so unusual sail settlements, and indeed evidence
of human habitation have been found. Perhaps these mounds rising above
the water table inspired the ancient belief of creation as having begun
on a mound of earth that emerged from the primordial waters of Nun
(Pyramid Text 600).































 The Nile is the longest river in the world,
stretching north for approximately 4,000 miles from East Africa to the
Mediterranean. Studies have shown that the River (Iteru, meaning,
simply, River, as the Map of the Nile RiverEgyptians called it)
gradually changed its location and size over millions of years. The Nile
flows from the mountains in the south to the Mediterranean in the
north. Egyptians traveling to other lands would comment on the "wrong"
flow of other rivers. For example, a text of Tuthmosis I in Nubia
describes the great Euphrates river as the "inverted water that goes
downstream in going upstream."
The Nile is the longest river in the world,
stretching north for approximately 4,000 miles from East Africa to the
Mediterranean. Studies have shown that the River (Iteru, meaning,
simply, River, as the Map of the Nile RiverEgyptians called it)
gradually changed its location and size over millions of years. The Nile
flows from the mountains in the south to the Mediterranean in the
north. Egyptians traveling to other lands would comment on the "wrong"
flow of other rivers. For example, a text of Tuthmosis I in Nubia
describes the great Euphrates river as the "inverted water that goes
downstream in going upstream."


 Angel Falls
or Kerepakupai merú (which means "
Angel Falls
or Kerepakupai merú (which means "













